Paper Details
| Authors | Hayder Al-Hraishawi, Mario Minardi, Houcine Chougrani, Oltjon Kodheli, Jesus Fabian Mendoza Montoya, Symeon Chatzinotas |
| Pulbication | IEEE Access |
| doi | 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3131030 |
Abstract
In this paper, we propose an approach for constructing a multi-layer multi-orbit space information network (SIN) to provide high-speed continuous broadband connectivity for space missions (nanosatellite terminals) from the emerging space-based Internet providers. This notion has been motivated by the rapid developments in satellite technologies in terms of satellite miniaturization and reusable rocket launch, as well as the increased number of nanosatellite constellations in lower orbits for space downstream applications, such as earth observation, remote sensing, and Internet of Things (IoT) data collection. Specifically, space-based Internet providers, such as Starlink, OneWeb, and SES O3b, can be utilized for broadband connectivity directly to/from the nanosatellites, which allows a larger degree of connectivity in space network topologies. Besides, this kind of establishment is more economically efficient and eliminates the need for an excessive number of ground stations while achieving real-time and reliable space communications. This objective necessitates developing suitable radio access schemes and efficient scalable space backhauling using inter-satellite links (ISLs) and inter-orbit links (IOLs). Particularly, service-oriented radio access methods in addition to software-defined networking (SDN)-based architecture employing optimal routing mechanisms over multiple ISLs and IOLs are the most essential enablers for this novel concept. Thus, developing this symbiotic interaction between versatile satellite nodes across different orbits will lead to a breakthrough in the way that future downstream space missions and satellite networks are designed and operated.
Summary
This paper describes a scenario, very close to ours. Where a satellite uses a megaconstellation to connect to the ground.
The main focuses of this paper is Radio Access and Routing.
Radio Access
For radio access they discuss beamforming and also discuss different multiplexing strategies for example: CDMA,TDMA, SDMA and NOMA.
There is no math, but the paper concludes that SIC multi-user detector for uplink along with NOMA concept for downlink probably makes sense.
Routing:
The paper focuses on Software Defined Networks.
For routing they separate the routing and the forwarding to two separate entities. In the paper this is called the controller and the switches.
The paper uses a framework called OpenFlow, for routing, and find that when the constellation constists of many satellites the control singalling grows a lot.
General Thoughts
A large focus on Radio Access and routing.
There seemes to be not that much math, and the paper doesnt go into that much detail.
Annotations
| Highlight Color | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Red | Aim to Improve |
| Yellow | Neutral comments |
| Green | Aim to replicate |
| Blue | Further Reading |
- “This will not only boost building a more connected world and bridge the digital divide across the globe [10] but also will enable satellite systems to compete with the terrestrial networks for provisioning long-distance backhaul and directly serving users with high-bandwidth links [11].” Page 2
- “In this setting, the nanosats of various downstream applications can be constantly connected to the Internet without depending on a large private or shared distributed network of ground stations, which will lead to more inexpensive and sustainable space systems by reducing the number of required ground stations while achieving reliable space communications” Page 2
- “Besides, from a network layer perspective, nanosat interconnections could be seen as a network slice of the NGSO constellations, which is already deployed for other application scenarios such as residential broadband, maritime, and aeronautical communications.” Page 2 - Er ikke helt sikker på jeg forstår hvad de prøver at fortælle her
- “However, interconnecting multiple satellite missions and constellations in an integrated fashion across multiple orbits will lead to a more densely and complex connected space information system for both radio access and backhauling.” Page 3
- “(a) space-based Internet access provisioning for nanosat terminals, (b) scalable space backhauling using multi-layer SINs.” Page 3 - Main focus of this paper
- “This architecture is particularly favorable for the areas where acquiring gateway sites is difficult [16].” Page 3 - A con against using traditional downlink methods
- “Additionally, this SIN structure will allow a satellite system to function strategically by transmitting TT&C data between nanosat terminals and network control center (NCC) on the ground, which will provide coordination and awareness of the operational characteristics about each counterpart system, and thus, accomplish a successful coexistence without imposing detrimental interference to their concurrent transmissions [17].” Page 3 - Argument for using new downlink
- “Additionally, some other research works focus on connecting the small satellites in the same orbit via a single-layer SIN. For example, the authors of [21] have proposed a self-organizing small satellite network architecture” Page 4
- “Reference [22] has proposed a double-layer satellite network to utilize both LEO and medium earth orbit (MEO) satellites with focusing on the coverage performance and network transmission delay.” Page 4
- “Earth and Space Observation: This is one of the widespread uses of satellite constellations in different orbits including capturing high-resolution images of earth and outer space, remote sensing in various frequencies, RF monitoring, global navigation satellite system (GNSS) reflectometry, etc. • Asset Tracking: Satellite payload in asset tracking projects consists of a device equipped with communication components to collect information sent from objects on ground and to transmit it back to ground stations. • Meteorology: Nanosats are able to play an important role in storm detection and in the development of climate and weather models that enhance weather forecasts. For instance, NASA RainCube project has started the testing phase for the location, tracking and analysis of rain and snowstorms over the entire earth. • Agriculture: Crop monitoring is another potential use of nanosats, where a better control of harvests, the improvement of the quality of agricultural products, the finding of diseases in crops, and analysis of the ramifications derived from the periods of drought can be facilitated by using nanosats. • Educational Activities: The development of scientific experiments outside the earth has become another common application of small satellites, which are unprecedented opportunities brought up by nanosats with their myriad possibilities. • Government Space Programs: The goals of these government programs varies from national security to emergency response. Some other useful applications can be for protecting the environment through detection of forest fires, studying the progress of melting ice, fighting against ocean pollution, detection of oil spills, monitoring of marine life, controlling of desertification, etc.” Page 4 - Different mission categories. Can be used to find missions which would benefit from new downlink.
- “However, realizing this concept faces many challenges from different aspects. Specifically, granting access for such a massive number of diversified users to the space-based Internet systems while taking into account the relative motion among different entities, variable QoS requirements, differential delays, and Doppler effects…are nontrivial tasks. Besides, networking and data packet routing of such a highly dynamic network considering the distinctive requirements of each information flow (e.g. TT&C versus observation data) need in-depth analysis of the communication protocols, ISL/IOL characteristics whether RF or optical, transmit power, bandwidth along with other system parameters.” Page 5 - Challenges of the proposed solution
- “Besides, the time division multiple access (TDMA) method has been also considered and standardized in DVB-RCS (Digital Video Broadcasting-Return Channel via Satellite)” Page 6 - Maybe figure out what DVB-RCS is used/made for?
- “In this context, the work in [24] has conducted a survey on the classical multiple access protocols highlighting their benefits and pitfalls from efficiency and scalability perspectives.” Page 6
- further_reading
- A work on RAN in the context of space
- “Reference [25] has studied the multiplexing schemes for a simple use case considering one GSO satellite relays data to 15 LEO satellites and proposed two multiple radio access: (a) multi-frequency TDMA (MF-TDMA) scheme used on the high-rate links and on the low-rate telemetry links and (b) TDMA for low rate tele-command link.” Page 6
- further_reading
- Also regarding RAN
- “Developing innovative radio access schemes for the multilayer SINs requires major research efforts due to the spatiotemporal heterogeneity of satellites across different orbits.” Page 6 - Why RAN is important to look into
- “The existing beamforming methods in ground-space integrated networks are performed at the user side but recently few satellite operators have shifted this process to the satellite side as in the recent advances employed by O3b mPower satellite constellation of SES and Starlink mega-constellation of SpaceX, where a dynamic digital beamforming is conducted at the satellites.” Page 6 - Starlink beamformer fra satelliten
- “In the latter case, the beamforming will rely on the knowledge/estimation of the channel state information (CSI) and its update rate [27],” Page 6
- further_reading,beamforming,CSI
- If the satellite has no prior knowledge of the position of the mega constellation
- “whereas in the former case, the satellite position relative to the antenna can be readily obtained by combining ephemeris information with geometrical modelling [28].” Page 6
- further_reading,beamforming
- If the satellite knows the position of the mega-constellation
- “Furthermore, every nanosat dictates the different type of requirement in the considered payload where three possible approaches can be highlighted; payload based on fixed beam antennas, flexible payload based on passive antennas with selectable apertures and steerable antennas, and flexible payload with reconfigurable active antennas” Page 6 - I don’t quite get this, but i maybe think it is important
- “NOMA can be incorporated in the multi-beam satellite architecture to design efficient transmission strategies that aim at increasing access network flexibility and capacity [29].” Page 6
- beamforming,NOMA,RAN
- NOMA in a beamforming scenario
 - We should probably do a figure similar to this
- We should probably do a figure similar to this
- “However, this is not always the case for nanosats, e.g. TT&C carriers need low-rate high-reliable links while sensor data requires high-rate downloads. This inconsistency in service demand is a crucial factor in selecting and designing proper access protocols.” Page 7
- QoS
- The variation of needs from satellites.
- “To this end, snapshot division is a useful method for dynamic topology access design, which divides the time-varying topology into a sequence of static snapshots [32].” Page 7 - For simulation they do the same as the other paper(On the use of mega constellations) using snapshots for the time-varying component
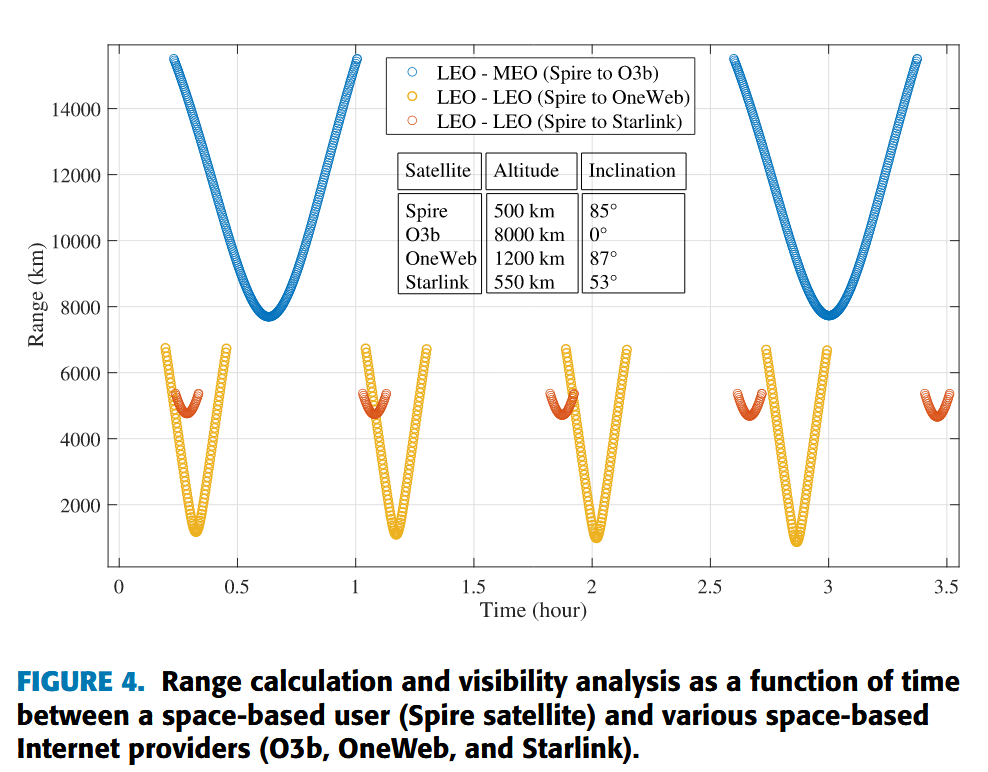
- “We have selected only one satellite from each constellation to analyze the visibility and periodicity with considering the distance variation as a function of time.” Page 7 - Seems like a pretty tough assumption
- “These approaches require each satellite to store the entire network topology along with the routing tables [24], but in a complex network, like our multi-layer SIN, it is difficult to maintain routing tables and consumes more power and bandwidth.” Page 7 - On routing
- “It has been extensively concluded that an effective solution is given by the well-known paradigm software-defined networking (SDN) [35].” Page 8
- further_reading,SDN
- Dont know the concept. Might be interesting further reading
- “n the literature, prior works in [36] and [37] have proposed to distribute an SDN controller on the ground, while some other works have considered the placement of the SDN controller on GSO satellites [38].” Page 8
- further_reading,SDN
- More on SDN
- “Authors in [40] have presented a detailed SDN structure adapted to the Internet of space things and nanosats but their implementation is more applicable for monitoring and Internet provisioning for remote areas, which make the developed platform terrestrial-dependent.” Page 8
- further_reading,SDN
- SDN for nanosats
- “Additionally, several well-developed network emulators and simulation tools such as Mininet and AGI STK alongside with the open-source SDN controller can be utilized for performance evaluation.” Page 8
- simulation_tools
- Potentielle ting til simulering
- “OpenFlow protocol [41] will facilitate SDN controllers to translate the computed data path into flow rules for the switches, enabling the packet forwarding toward the following hop.” Page 9
- further_reading,routing
- Openflow
- “innovative research directions can be inspired by utilizing the proposed concept such as empowering satellite constellations with storage and processing capabilities in a virtualized manner but that would lead to even more complicated slicing scenarios.” Page 10 - A proposal for future work could be for the megaconstellation to not only deliver connectivity but also compute and storage